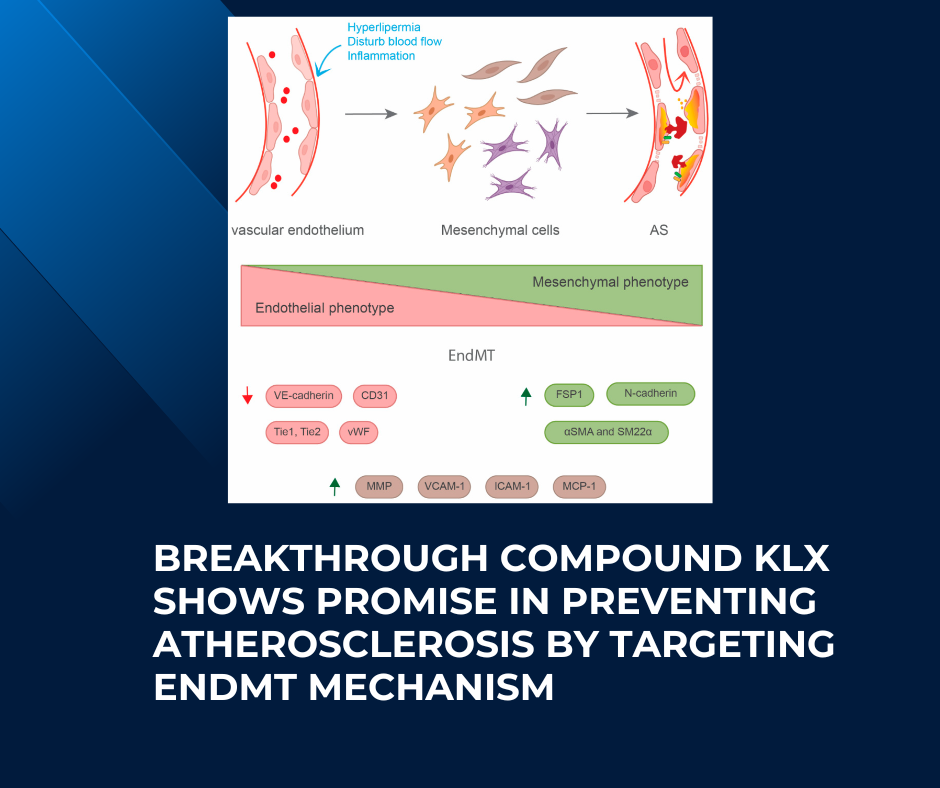
Atherosclerosis, a condition marked by the buildup of lipids and inflammatory cells in arterial walls, is a major cause of cardiovascular events. A key mechanism driving atherosclerosis is the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT), where endothelial cells transform into mesenchymal cells, contributing to plaque formation and vascular dysfunction. The novel anthraquinone compound, Kanglexin (KLX), has been studied for its ability to prevent EndMT in atherosclerosis by targeting fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 (FGFR1) and inhibiting the integrin β1/transforming growth factor-beta (TGFβ) signaling pathway. This research sheds light on the molecular mechanisms by which KLX exerts protective effects against EndMT and atherosclerotic progression.
The study focused on examining the impact of KLX on human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) undergoing TGFβ1-induced EndMT and on atherosclerotic lesions in ApoE-/- mice fed a high-fat diet. KLX was found to reduce morphological changes, decrease collagen synthesis, and restore cell-cell adhesion in TGFβ1-treated HUVECs. Additionally, KLX reversed the downregulation of endothelial markers and the upregulation of mesenchymal markers, indicating its potential to prevent EndMT. In vivo, KLX treatment decreased lipid accumulation, plaque formation, and collagen production in the aortic roots of mice, suggesting its effectiveness in reducing aortic EndMT and atherosclerosis.
The molecular mechanisms underlying KLX’s action were further explored, revealing that KLX activates FGFR1, which in turn activates MAP4K4, leading to the inhibition of integrin β1 and the suppression of the TGFβ receptor (TGFβR)/Smad signaling pathway. This cascade of signaling events results in the inhibition of EndMT. Activation of FGFR1 by KLX was confirmed by observing increased interactions between phosphorylated FGFR1 and MAP4K4, while inhibiting this pathway with an FGFR1 inhibitor reversed the effects of KLX. These results highlight KLX’s role in modulating key signaling pathways involved in EndMT and atherosclerosis, presenting a potential therapeutic approach for these conditions.
In summary, KLX provides protective effects against EndMT and atherosclerosis by activating the FGFR1/MAP4K4 pathway and inhibiting the integrin β1/TGFβ signaling pathway. The findings of this study position KLX as a promising candidate for the prevention and treatment of vascular EndMT and atherosclerosis, with potential clinical applications in managing cardiovascular diseases.